Synapse Link is a great capability, and with the recent news from Microsoft published today, it got even better: Now you can link your Dataverse and Fabric together and query directly from within your Fabric workspace. The best part? It’s completely managed. Apart from a few clicks, you don’t need to do a thing.
Here’s the announcement link: https://blog.fabric.microsoft.com/en-gb/blog/microsoft-onelake-adds-shortcut-support-to-power-platform-and-dynamics-365?ft=All&ref=thatbluecloud.com
I’ll be keeping this article up-to-date with new capabilities added, or new benefits & drawbacks I encounter.
There’s a link at the bottom of this article for a detailed guide from Microsoft.
Setting It Up
For us to establish connection, we need to set it up from both ends. First, we start from the Power BI / Fabric dashboard. Let’s go through the steps:
- Go to your Power BI dashboard, click the gear icon on the top right, and choose Manage Connections and Gateways.
- Add a new Cloud connection and choose Dataverse as the type.
- Get your Dataverse Environment URL from your Power Platform Admin Centre, copy it without any
https://parts into both Connection Name and Environment Domain fields. - Choose OAuth 2 as the authentication method, click Edit Credentials, set it up.
- Feel free to choose other boxes, such as Direct Query AAD Support.
- Save the form.
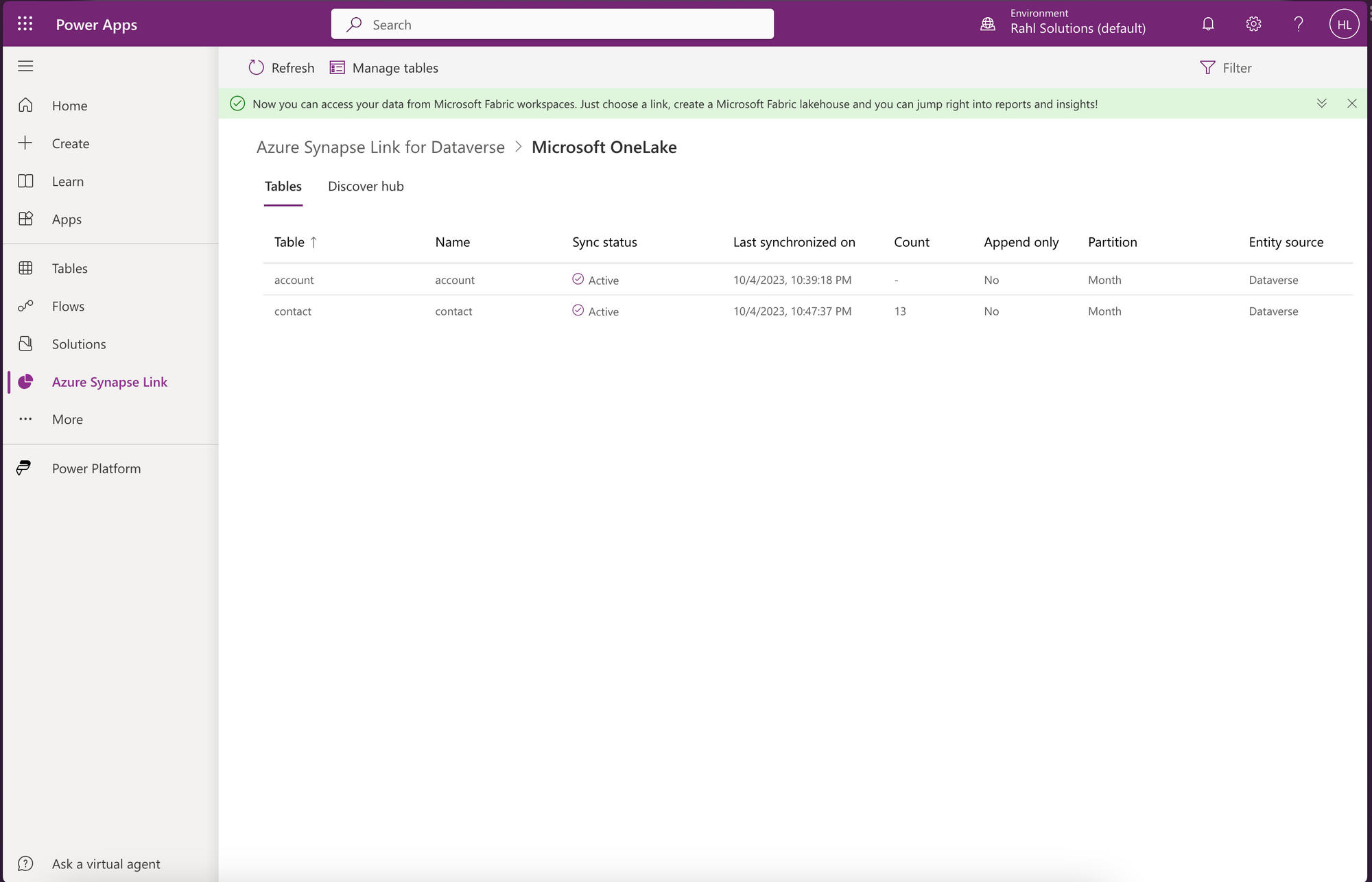
- Go to your tables, choose one with data. If you’re using the sample Microsoft Dynamics dataset, choose Contact. It has 13 records in it.
- Choose Export > Link to Microsoft Fabric (Preview) button.
- It’ll automatically create a Workspace in Fabric, and a Lakehouse in it.
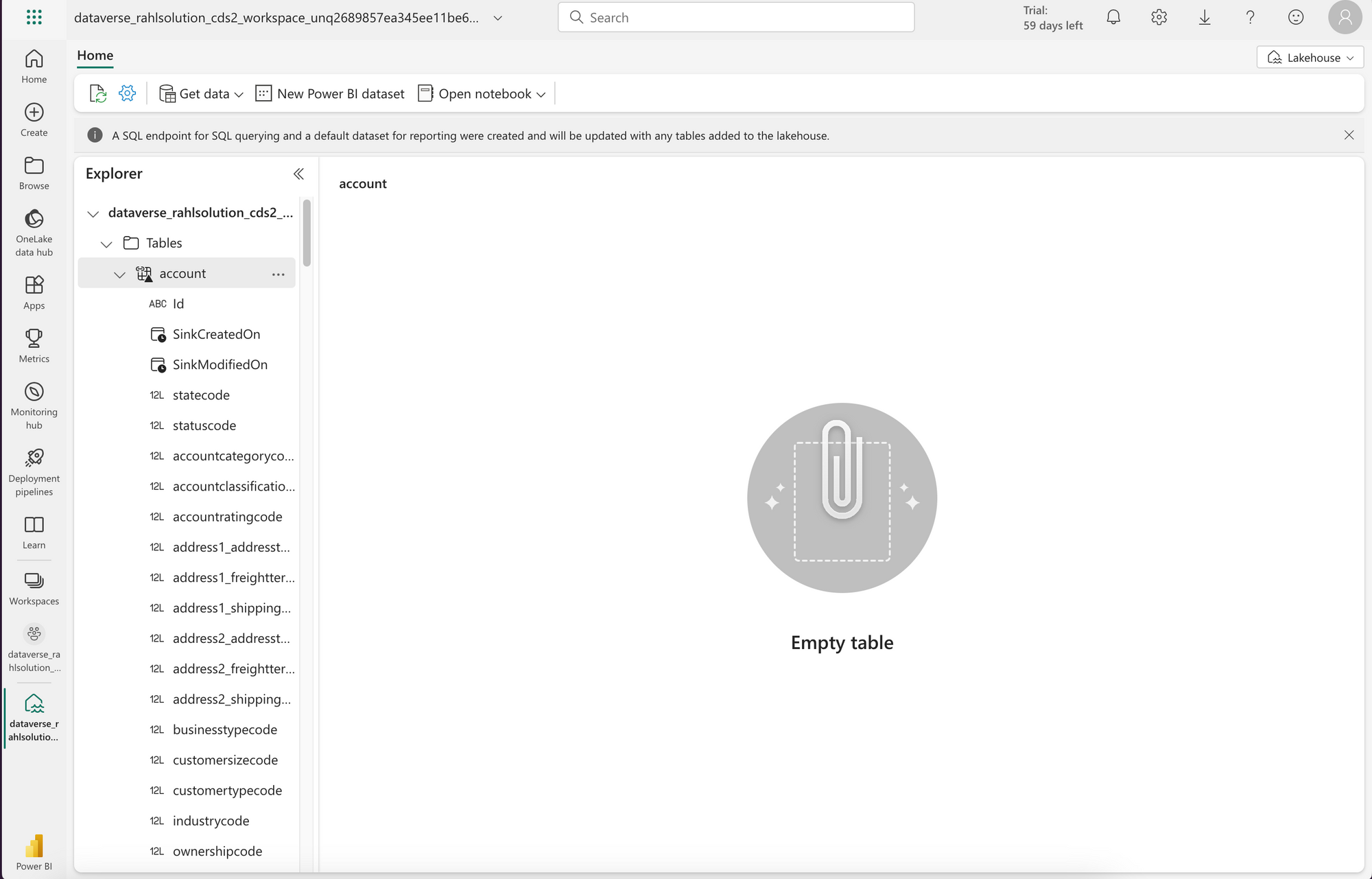
- You can go to the Lakehouse right away, but you might encounter
Path not founderror or the tables might show up underUndefinedschema. This is okay, just wait for about 10 minutes for it to properly build the tables. - Then you can go and query the data.
Benefits
- Completely SaaS. You don’t need to do much.
- In Synapse Link with Data Lake or Synapse Analytics, the files were created as CSV format. But with Fabric the files are created in Delta/Parquet format. So they are automatically recognised by Fabric as tables and works performantly.
Drawbacks
- It’ll only keep the last two years of data in the Lakehouse, based on the record created date. This is to optimise the performance, but keep it in mind.
- Very, very preview feature. It may change dramatically in the future.
About the Author:
I’m a cloud solutions architect with a coffee obsession. Have been building apps and data platforms for over 18 years, I also blog on Azure & Microsoft Fabric. Feel free to say hi on Twitter/X!
Reference: